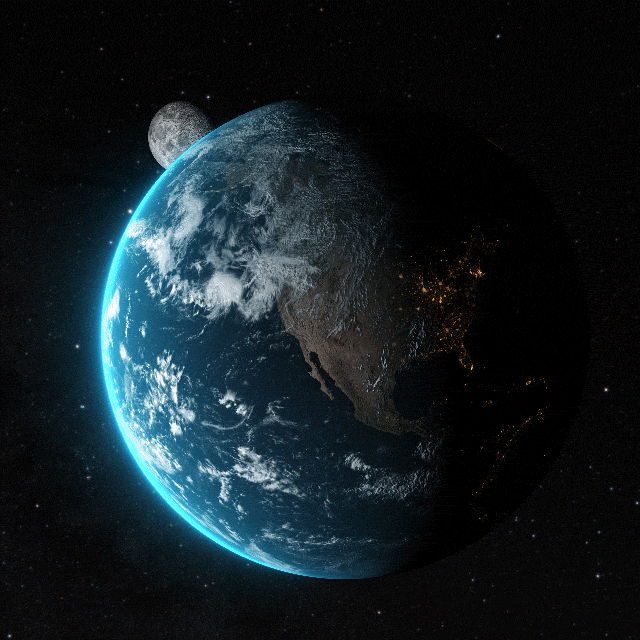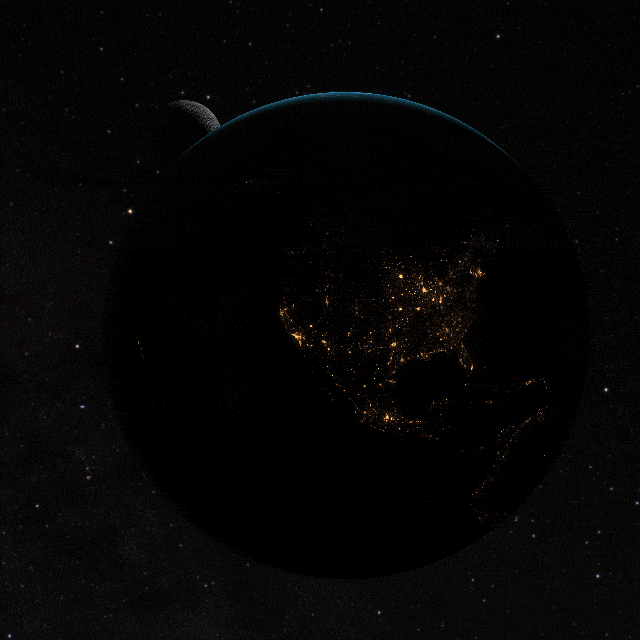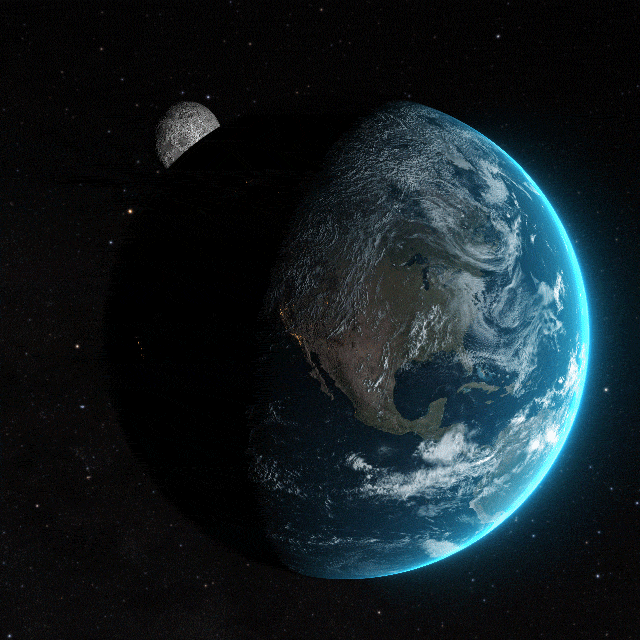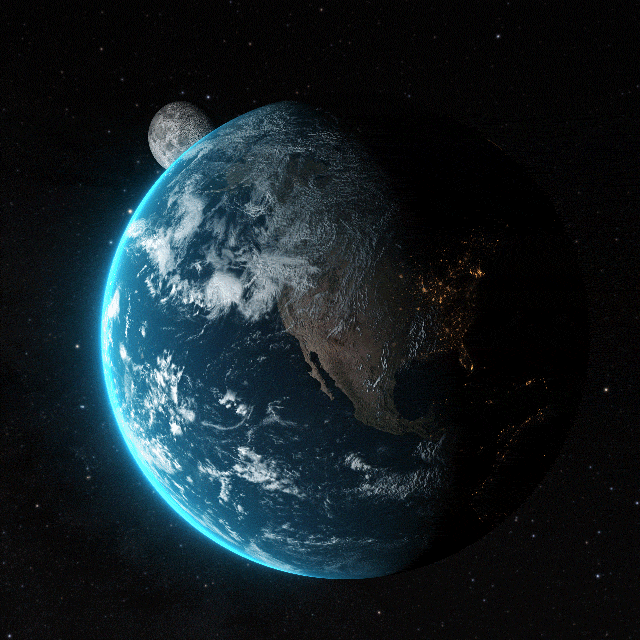
Earth, the third planet from the Sun, is a unique celestial body distinguished by its capacity to support life. Formed over 4.5 billion years ago through the accretion of cosmic dust and gas, it's the densest planet in the Solar System. Earth's gravitational pull interacts dynamically with other objects in space, most notably the Sun and its natural satellite, the Moon. This interaction governs phenomena such as tides and stabilizes Earth's axial tilt, contributing to the planet's climate stability.
The planet's surface is predominantly covered by water, with approximately 71% consisting of oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, and other bodies of water, which play a crucial role in Earth's climate and ecosystems. The remaining 29% is land, comprising continents and islands that exhibit a diverse array of geological features. Earth's lithosphere is segmented into several tectonic plates that slowly move across the asthenosphere, a process that shapes the planet's surface through continental drift, mountain formation, and seismic activity.
5 Fun Facts About Earth
- Earth is not a perfect sphere; it is an oblate spheroid, slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator due to its rotation.
- The Earth's atmosphere is composed mainly of nitrogen (about 78%) and oxygen (about 21%), which is essential for supporting life.
- Earth has a powerful magnetic field, generated by the movement of molten iron in its outer core, which protects the planet from harmful solar radiation.
- A day on Earth is not exactly 24 hours; it's slightly less, about 23 hours and 56 minutes, which is known as a sidereal day.
- The highest point on Earth is Mount Everest, and the lowest point is the Mariana Trench, showcasing the planet's extreme variations in elevation.